As a key component of the transmission system, the 420 clutch assembly plays an important role in connection, separation and overload protection during the power transmission process. The performance of the clutch assembly directly affects the vehicle's starting, shifting smoothness and power output efficiency. Once a fault occurs, it will not only reduce the driving experience, but may also cause more serious mechanical problems. Therefore, mastering the correct diagnosis method of common faults of the 420 clutch assembly is crucial to ensure the normal operation of the vehicle.
1. Basic structure and working principle of the 420 clutch assembly
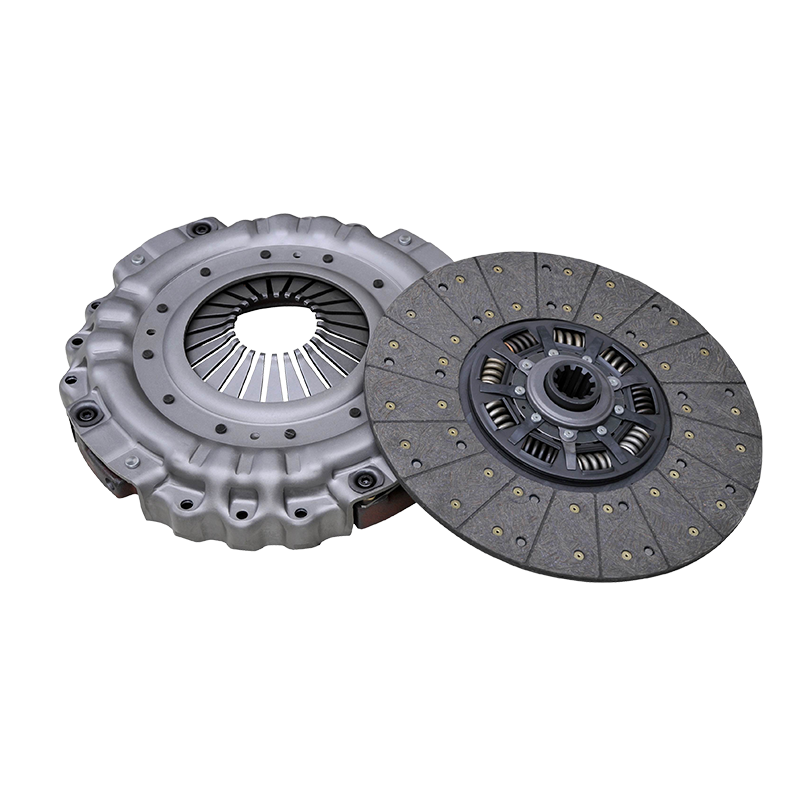
The 420 clutch assembly is mainly composed of an active part, a driven part, a clamping mechanism and an operating mechanism. The active part is connected to the engine flywheel, including components such as the flywheel, the pressure plate and the clutch cover; the driven part consists of a driven plate and a driven shaft, which is responsible for transmitting power to the transmission; the clamping mechanism presses the pressure plate to the flywheel through a diaphragm spring or a coil spring, so that the driven plate is clamped between the two to achieve power transmission; the operating mechanism controls the separation and combination of the clutch.
When the engine is running, the active part rotates with the flywheel. When the driver steps on the clutch pedal, the operating mechanism overcomes the pressure of the compression spring, causing the pressure plate to move backward, the driven plate to separate from the flywheel, and the power transmission is interrupted; when the clutch pedal is released, the compression spring causes the pressure plate to re-compress the driven plate, and the engine power is transmitted to the driven plate through the friction torque, and then to the transmission.
2. Common fault types and diagnostic procedures
(I) Clutch slippage
Fault phenomenon: When the vehicle starts, the car still cannot start normally after the clutch pedal is completely released; during driving, the engine speed increases during acceleration, but the vehicle speed increases slowly; when climbing a hill with a heavy load, it is obvious that the power is insufficient.
Diagnostic steps
Check the free travel of the clutch pedal: Under normal circumstances, the clutch pedal should have a certain free travel. If the free travel is too small or absent, the pressure plate will not be able to fully compress the driven plate, causing slippage. Use a ruler to measure the pedal free travel. If it does not meet the value specified in the vehicle maintenance manual, it needs to be adjusted.
Check the wear of the clutch plate: Check the degree of wear of the clutch plate through the observation hole or remove the clutch bottom cover. If the friction lining of the clutch plate is severely worn, the thickness is less than the specified value, or the friction lining surface is charred or hardened, the friction torque will be reduced and slipping will occur. At this time, the clutch plate needs to be replaced.
Check the surface condition of the pressure plate and flywheel: If there are grooves, uneven wear or ablation on the surface of the pressure plate and flywheel, it will affect the fit with the clutch plate and cause slipping. If the damage is minor, it can be repaired by polishing; if the damage is serious, the pressure plate or flywheel needs to be replaced.
Check the clamping spring: If the diaphragm spring or coil spring is broken or the elastic force is weakened, the clamping force will be insufficient, causing the clutch to slip. The spring elastic force tester can be used to test the spring elastic force. If it does not meet the standard, the spring should be replaced.
(II) Incomplete clutch separation
Fault phenomenon: After pressing the clutch pedal, it is difficult to shift gears, accompanied by the sound of gear collision; after barely shifting gears, without lifting the clutch pedal, the vehicle tends to rush forward, and even stalls.
Diagnostic steps
Check the clutch pedal free travel: If the free travel is too large, the release bearing will not be able to push the pressure plate enough, resulting in the clutch not being able to be completely separated. Adjust the pedal free travel according to the maintenance manual. If the fault persists after adjustment, proceed to the next step.
Check the clutch hydraulic control system: For hydraulically operated clutches, check whether the brake fluid level is normal and whether there is leakage, blockage or air in the pipeline. If the brake fluid is insufficient, add it to the specified level; if there is a leak in the pipeline, repair the leaking part; if there is air in the pipeline, perform exhaust operation to exhaust the air.
Check the release lever or release bearing: Remove the clutch bottom cover and check whether the release lever is deformed or worn, and whether the release bearing is damaged or stuck. If the release lever height is inconsistent, adjust the height of the release lever to meet the specified value; if the release bearing is damaged, replace the release bearing.
Check the driven disc: Warping of the driven disc, loose rivets, or too tight fit between the spline hub and the transmission input shaft will hinder the movement of the driven disc and result in incomplete separation. If problems are found in the driven disc, repair or replace it according to the specific situation.
(III) Clutch abnormal noise
Fault phenomenon: abnormal noises, such as "rustling" and "clicking", are heard during the process of pressing or releasing the clutch pedal.
Diagnostic steps
Judge the timing of abnormal noises: abnormal noises occur when the clutch pedal is pressed and disappear after release, which may be caused by damage to the release bearing or poor lubrication; if abnormal noises are heard at the moment of clutch engagement or separation, it may be caused by looseness or wear of the release lever, driven plate or pressure plate.
Check the release bearing: start the engine and slowly press the clutch pedal. If you hear a "rustling" sound, and the sound increases as the pedal is pressed, it is likely that the release bearing is worn or lacks lubrication. At this time, apply an appropriate amount of grease on the release bearing seat. If the abnormal noise disappears, it means that there is a lubrication problem; if the abnormal noise still exists, the release bearing needs to be replaced.
Check the driven plate: disassemble the clutch and check whether the rivets on the driven plate are loose and whether the shock absorber spring is broken or fallen off. If these problems exist, the driven plate will vibrate when it rotates and make abnormal noises. The driven plate should be replaced.
Check the pressure plate and clutch cover: Check whether the fixing bolts of the pressure plate and clutch cover are loose, and whether the internal parts are worn or damaged. If they are loose, tighten the bolts; if the parts are damaged, replace them.
(IV) Clutch shaking
Fault phenomenon: When the vehicle starts, the clutch engagement is not stable, and the body shakes significantly; shaking may also occur during the gear shifting process.
Diagnostic steps
Check the engine fixing: Loose engine fixing bolts or damaged brackets will cause the engine to vibrate during operation and transmit it to the clutch, causing the clutch to shake. Check whether the engine fixing bolts are tightened and whether the brackets are cracked or deformed. If there are any problems, repair or replace them.
Check the clutch plate and pressure plate: The surface of the clutch plate is uneven, oily or hardened, and the surface of the pressure plate is warped and deformed, which will cause uneven force when the clutch is engaged, causing shaking. Check the surface condition of the clutch plate and pressure plate. If there are any problems, replace them according to the actual situation.
Check the fit between the spline hub of the driven disc and the input shaft of the transmission: If the fit clearance is too large or too tight, it will affect the normal rotation of the driven disc and cause the clutch to tremble. Measure the fit clearance. If it does not meet the standard, adjust or replace the relevant parts.
Check the flywheel working surface: If there are grooves, wear or excessive runout on the flywheel working surface, it will cause vibration when the clutch is engaged. Use a dial indicator to measure the runout of the flywheel. If it exceeds the specified value, it can be repaired by polishing or replaced.
3. Reasonable use of diagnostic tools and equipment
When diagnosing 420 clutch assembly failures, some professional tools and equipment are needed. Commonly used tools include rulers, dial indicators, spring force testers, wrenches, etc. Rulers are used to measure the free travel of the clutch pedal; dial indicators can be used to detect the runout of components such as flywheels and pressure plates; spring force testers are used to detect the elastic force of the compression spring; wrenches are used to disassemble and install clutch-related components.
In addition, for hydraulically operated clutch systems, it is also necessary to use brake fluid filling machines, pipeline pressure testers and other equipment to accurately detect the pressure and sealing of the hydraulic system. When using these tools and equipment, strictly follow the operating procedures to ensure the accuracy of the measurement data and the safety of the operation.
4. Diagnostic precautions
Before performing fault diagnosis, you should understand the vehicle's usage, the process and symptoms of the fault in detail so that you can conduct a more targeted inspection.
When disassembling the clutch assembly, make sure to mark it to ensure that the position of each component is accurate during installation to avoid new faults caused by improper installation.
During the diagnosis process, pay attention to safety to prevent burns or pinching from the engine, transmission components, etc.
When replacing clutch components, you should choose accessories of qualified quality and install and adjust them strictly in accordance with the requirements of the maintenance manual.
 English
English русский
русский




 English
English  No.25, Hu Chuang Road, New District Industrial Park, Suzhou, Jiangsu, China.
No.25, Hu Chuang Road, New District Industrial Park, Suzhou, Jiangsu, China.  +86-13338663262
+86-13338663262 
