Proper alignment of a 430mm Jinlong Bus Push Clutch Disk Assembly Kit is essential to ensure the smooth operation and longevity of a bus’s transmission system. Misalignment can lead to uneven wear, reduced performance, and even premature failure of the clutch assembly.
Understanding the 430mm Jinlong Bus Push Clutch Disk Assembly Kit
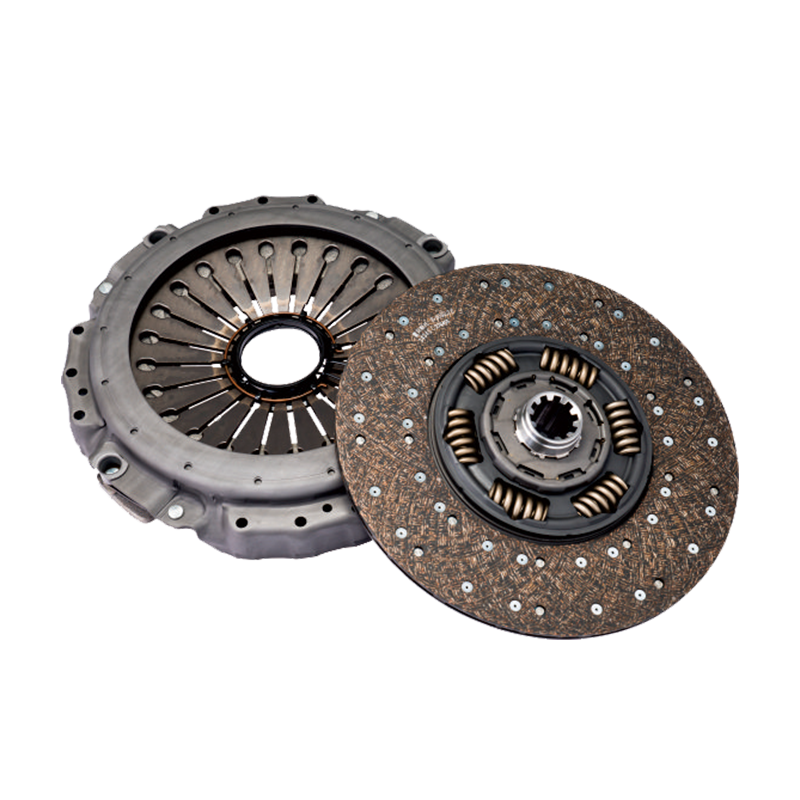
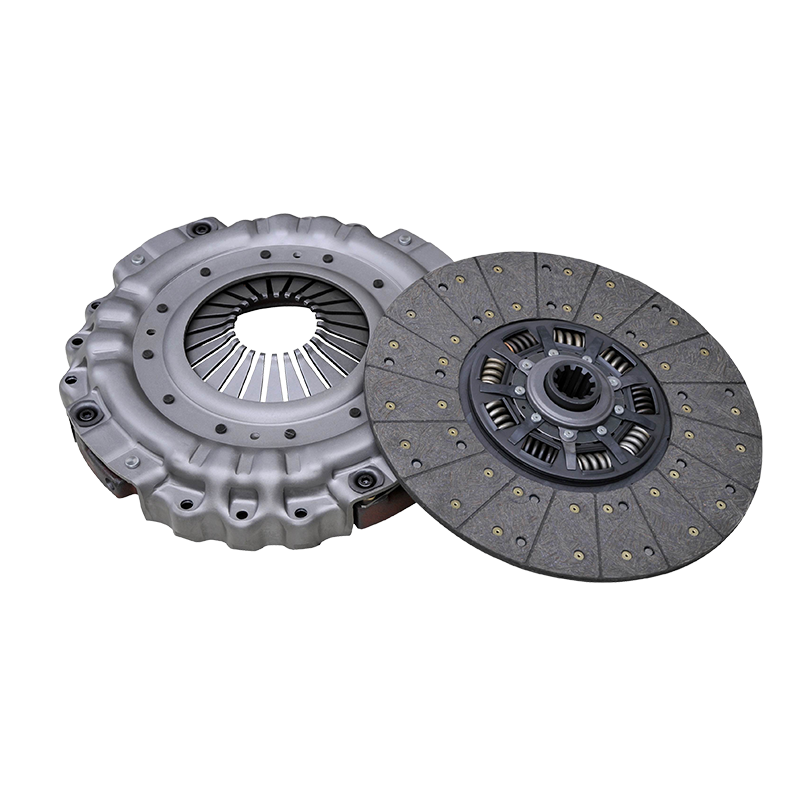
The 430mm Jinlong Bus Push Clutch Disk Assembly Kit consists of a clutch disk, pressure plate, release bearing, and related fasteners. Each component is designed to transfer engine torque smoothly to the transmission while minimizing vibration and wear. The clutch disk itself is a critical element that engages and disengages the engine from the drivetrain. Proper alignment ensures that the friction surfaces make consistent contact and the clutch pedal feel remains uniform.
Key components of the 430mm Jinlong Bus Push Clutch Disk Assembly Kit include:
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Clutch disk | Transfers engine torque to transmission |
| Pressure plate | Applies force to clutch disk for engagement |
| Release bearing | Facilitates smooth pedal operation |
| Alignment tools | Assists in centering the disk during installation |
Ensuring correct alignment begins with understanding how these components interact. Misalignment can occur due to improper installation, worn components, or uneven fastening of bolts.
Tools Required for Alignment Checking
Accurate checking of a 430mm Jinlong Bus Push Clutch Disk Assembly Kit requires specialized tools. The selection of the right tools reduces the risk of errors during installation and ensures the transmission system operates efficiently.
The essential tools include:
| Tool | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Dial indicator | Measures run-out and axial displacement |
| Clutch alignment tool | Centers the clutch disk during installation |
| Torque wrench | Ensures correct fastener tension |
| Straightedge or ruler | Checks radial alignment relative to flywheel |
| Inspection mirror | Assists in viewing hard-to-reach areas |
Each tool plays a specific role. For instance, the clutch alignment tool is essential to maintain the disk’s central position relative to the flywheel. Dial indicators are used to check axial and radial run-out, which can indicate misalignment.
Visual Inspection Before Alignment
Before using any measurement tools, a visual inspection is recommended. Look for obvious signs of wear or damage on the clutch disk, pressure plate, and surrounding components. Pay attention to:
- Clutch disk surface – Check for grooves, scoring, or uneven friction material wear.
- Pressure plate – Look for warping or heat spots, which can affect alignment.
- Flywheel surface – Ensure it is smooth, free from cracks, and properly machined.
- Fasteners – Verify bolts are in good condition and correctly threaded.
A thorough visual inspection helps identify potential alignment issues before they escalate into operational problems.
Step-by-Step Procedure for Checking Alignment
1. Centering the clutch disk
Begin by inserting the clutch alignment tool through the center hub of the clutch disk. Ensure that it aligns with the pilot bearing or bushing in the flywheel. This step prevents lateral movement and ensures that the clutch disk is concentric with the flywheel.
2. Tightening the pressure plate
Once the disk is centered, gradually tighten the pressure plate bolts in a crisscross pattern to avoid uneven pressure. Use a calibrated torque wrench and follow the manufacturer’s specified torque values. Improper tightening can shift the disk, causing misalignment.
3. Checking radial alignment
Use a straightedge or ruler to measure the radial alignment of the disk relative to the flywheel. The clutch disk should sit evenly without any noticeable tilt. A slight radial deviation is acceptable, but it should not exceed the tolerance recommended by the manufacturer.
4. Measuring axial run-out
Attach a dial indicator to a stable reference point on the engine block and position the tip against the surface of the clutch disk. Rotate the disk slowly while monitoring the indicator. The axial run-out should fall within the specified limits; excessive run-out indicates that the disk is not properly aligned or the flywheel may be warped.
5. Verifying engagement and pedal feel
After installation, operate the clutch pedal and observe the engagement point and pedal travel. Inconsistent engagement or unusual vibration can signal misalignment. Make adjustments as needed before fully securing the assembly.
Common Alignment Issues and Causes
Misalignment of a 430mm Jinlong Bus Push Clutch Disk Assembly Kit can occur due to multiple factors:
- Improper centering of the disk – If the clutch alignment tool is not used, the disk may shift laterally.
- Warped flywheel – Heat and wear can cause uneven surfaces, affecting alignment.
- Uneven bolt tightening – Fasteners tightened in a random sequence can tilt the pressure plate.
- Worn pilot bearing – A loose or damaged pilot bearing allows the clutch hub to move off-center.
- Foreign particles – Dirt or debris between the disk and flywheel can prevent proper seating.
Identifying these root causes early helps prevent premature clutch failure and ensures a longer service life.
Best Practices for Maintaining Alignment
Maintaining the alignment of a 430mm Jinlong Bus Push Clutch Disk Assembly Kit is critical for reliable bus operation. Recommended practices include:
- Always use a new clutch alignment tool during installation.
- Inspect the flywheel and pressure plate for wear and warping before assembly.
- Follow a crisscross torque pattern to avoid uneven pressure.
- Conduct periodic inspections of axial and radial run-out.
- Replace worn pilot bearings and fasteners when necessary.
These practices reduce the risk of misalignment and improve drivetrain performance and reliability.
Inspection Checklist for Alignment Verification
To ensure no step is overlooked, the following checklist can guide the alignment verification process:
| Step | Task | Acceptable Condition |
|---|---|---|
| Visual inspection | Check clutch disk, pressure plate, and flywheel | No grooves, cracks, or warping |
| Centering | Insert alignment tool through hub | Disk centered in pilot bearing |
| Bolt tightening | Crisscross torque to specified value | Even pressure distribution |
| Radial alignment | Measure with straightedge | Disk sits flat without tilt |
| Axial run-out | Use dial indicator | Within manufacturer tolerance |
| Pedal test | Operate clutch pedal | Smooth engagement, no vibration |
Following a structured checklist ensures consistent and reliable alignment across different service operations.
Effects of Misalignment on Bus Performance
Misalignment of a 430mm Jinlong Bus Push Clutch Disk Assembly Kit can negatively affect various aspects of bus performance:
- Increased wear – Uneven pressure on the disk and pressure plate accelerates wear.
- Vibration – Misalignment can lead to clutch chatter or pedal vibration.
- Gear engagement issues – Poor alignment may result in hard or incomplete gear shifts.
- Reduced fuel efficiency – Inefficient torque transfer can increase engine load.
Addressing alignment issues promptly ensures operational safety and cost efficiency.
Advanced Measurement Techniques
For buses with high mileage or heavy-duty operation, advanced measurement techniques can provide more precise alignment data:
- Laser alignment systems – Offer highly accurate measurement of radial and axial displacement.
- Electronic dial indicators – Capture run-out digitally for detailed analysis.
- Thermal imaging – Detects hotspots indicating uneven clutch pressure.
Using these advanced techniques complements traditional tools and improves diagnostic accuracy.
Case Study: Alignment Verification in Heavy-Duty Buses
A fleet operator performing routine maintenance on buses equipped with a 430mm Jinlong Bus Push Clutch Disk Assembly Kit observed unusual pedal vibration. A detailed alignment check using a dial indicator revealed a 0.4 mm axial deviation, exceeding recommended tolerance. Re-centering the disk with a clutch alignment tool and proper torqueing restored smooth operation. This case demonstrates the importance of precision alignment in maintaining clutch performance.
Summary
Checking the alignment of a 430mm Jinlong Bus Push Clutch Disk Assembly Kit is a multi-step process that requires careful attention to detail, proper tools, and structured inspection methods. Key takeaways include:
- Proper centering using a clutch alignment tool is essential.
- Gradual and even tightening of bolts prevents tilting of the pressure plate.
- Both radial and axial run-out should be measured to confirm alignment.
- Visual inspections and pedal tests complement mechanical measurements.
- Misalignment can lead to accelerated wear, vibration, and performance loss.
Implementing these procedures ensures that the 430mm Jinlong Bus Push Clutch Disk Assembly Kit operates efficiently, extends service life, and maintains bus drivability.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1: How often should the alignment of a 430mm Jinlong Bus Push Clutch Disk Assembly Kit be checked?
A1: Alignment should be checked during every clutch replacement or when symptoms such as pedal vibration or hard gear shifts appear.
Q2: Can I check alignment without a clutch alignment tool?
A2: While minor checks can be done visually, accurate alignment requires a clutch alignment tool to center the disk properly.
Q3: What tolerance is acceptable for axial run-out?
A3: Axial run-out should follow the manufacturer’s specifications, typically within 0.2–0.5 mm depending on bus type and service conditions.
Q4: Is radial misalignment reversible after installation?
A4: Yes, but it may require loosening the pressure plate, re-centering the clutch disk, and retightening bolts according to proper torque specifications.
Q5: Can misalignment affect the lifespan of the entire transmission system?
A5: Absolutely. Misalignment increases stress on the clutch and transmission components, potentially leading to premature wear and failure.
References
- Automotive Clutch Systems: Principles, Maintenance, and Troubleshooting. SAE International, 2020.
- Bus Maintenance Manual: Transmission and Clutch Guidelines, Department of Transportation, 2021.
- Heavy-Duty Vehicle Clutch Alignment Procedures, Fleet Maintenance Journal, 2019.
 English
English русский
русский




 English
English  No.25, Hu Chuang Road, New District Industrial Park, Suzhou, Jiangsu, China.
No.25, Hu Chuang Road, New District Industrial Park, Suzhou, Jiangsu, China.  +86-13338663262
+86-13338663262 
