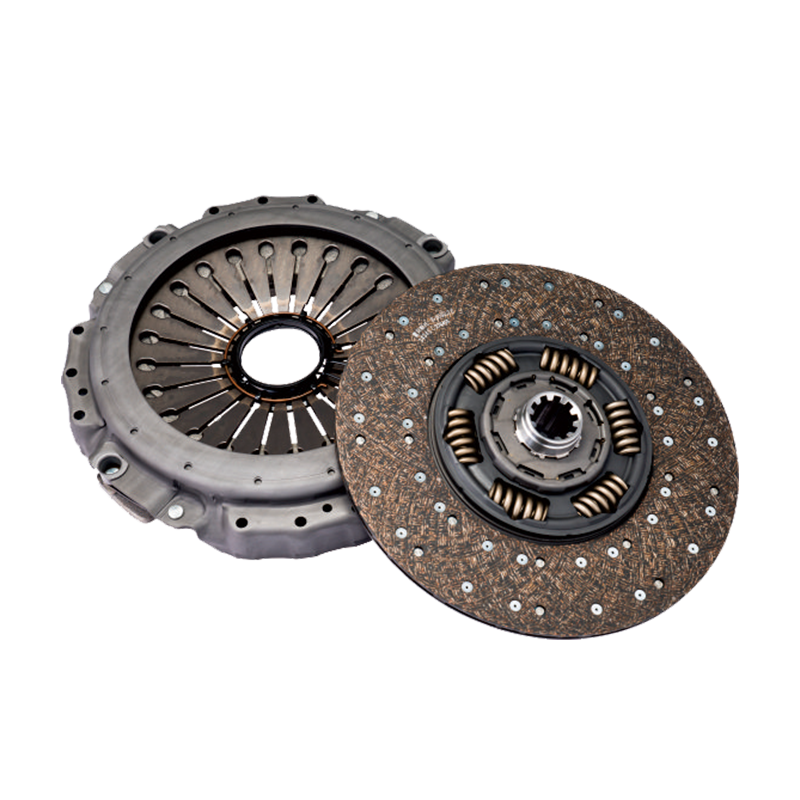
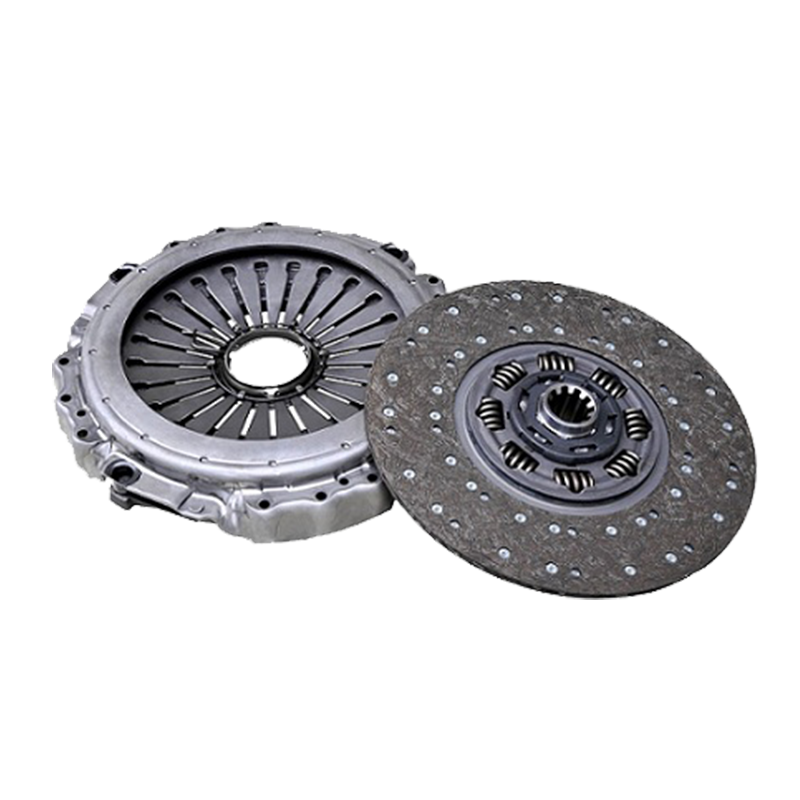
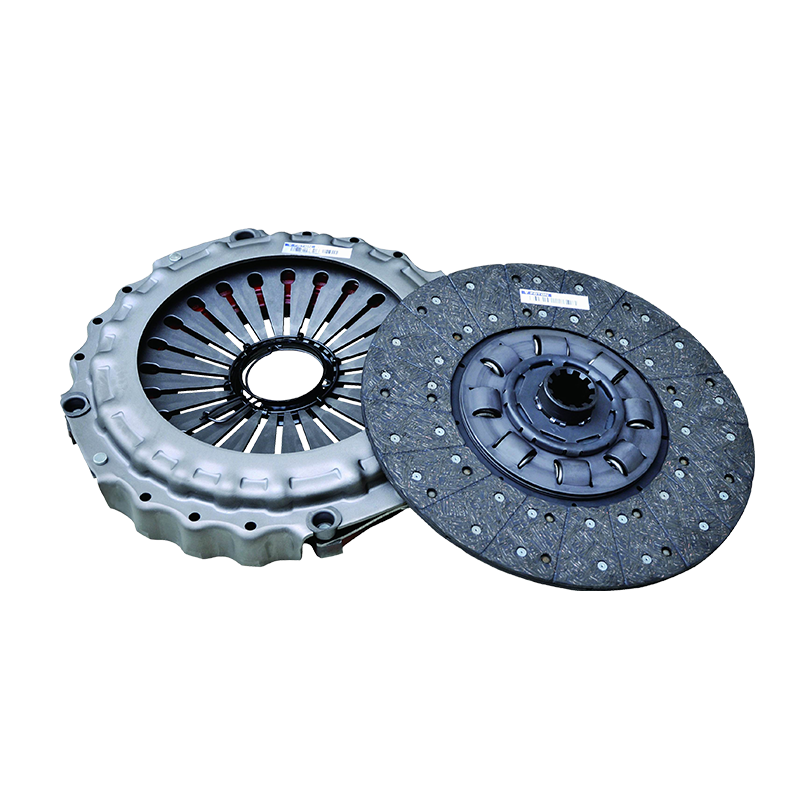
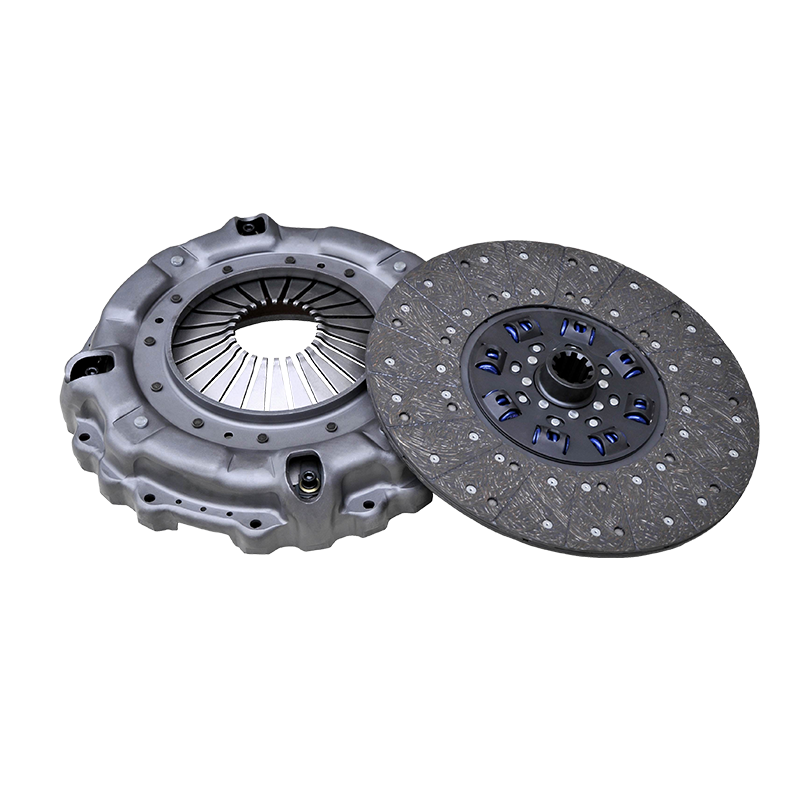
The reliable transfer of immense engine power to the drivetrain is a fundamental requirement for any heavy-duty truck designed to handle demanding loads and challenging terrains. At the heart of this power transmission system in many robust vehicles lies a critical component: the 430mm pull clutch assembly for shaanxi automobile delong vehicles. Understanding its operation is not merely an academic exercise; it is essential for fleet managers, maintenance technicians, and procurement specialists to make informed decisions regarding maintenance, repair, and overall vehicle performance.
The Fundamental Principles of a Pull-Type Clutch System
Before delving into the specifics of the 430mm pull clutch assembly for shaanxi automobile delong vehicles, it is crucial to establish a foundational understanding of what a pull-type clutch is and how it fundamentally differs from other designs. A clutch’s primary function is to connect and disconnect the engine’s rotating power from the transmission, and subsequently, the wheels. This allows for smooth vehicle launch, seamless gear changes, and the ability to bring the vehicle to a stop without stalling the engine.
The key differentiator for a pull-type clutch lies in the direction of force applied to the release mechanism. In a more common push-type clutch, the release bearing is pushed forward towards the transmission to disengage the clutch. In contrast, a pull-type clutch system operates in the reverse manner. Here, the release bearing is pulled away from the transmission, towards the rear of the vehicle, to achieve disengagement. This seemingly simple reversal in action has significant implications for the assembly’s design, performance, and durability, which we will explore in subsequent sections. This design is particularly advantageous in applications where high torque loads are present, as it allows for a more robust and compact release mechanism that can handle greater forces without compromising function. The 430mm pull clutch assembly for shaanxi automobile delong vehicles is engineered precisely with this high-torque environment in mind, providing a reliable link between a powerful engine and a heavy-duty transmission.
Core Components of the 430mm Pull Clutch Assembly
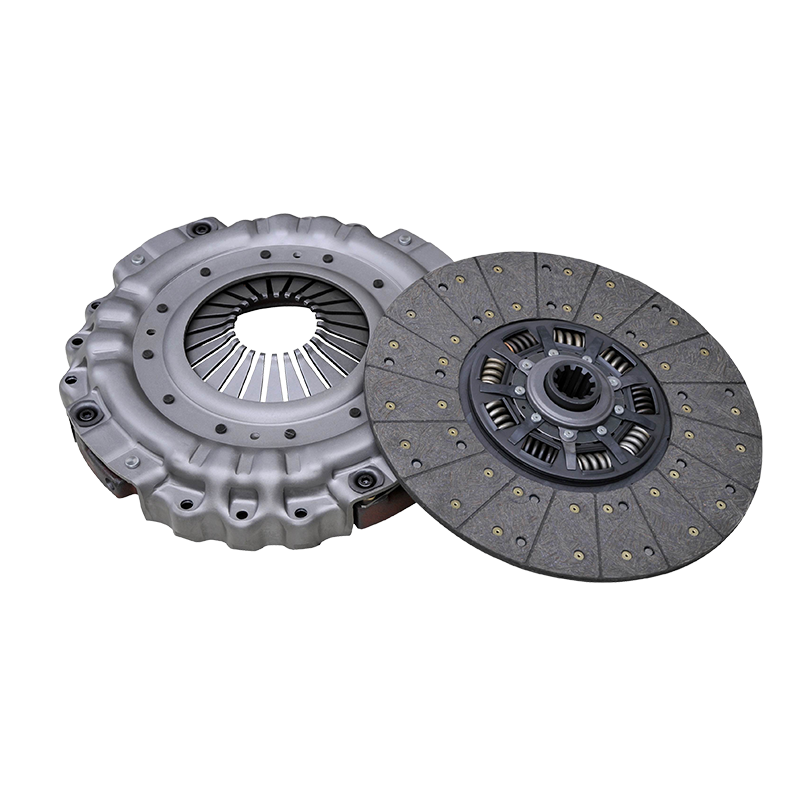
To fully comprehend how the assembly works, one must first be familiar with its key constituent parts. Each component plays a specific and vital role in the seamless operation of the whole. The 430mm pull clutch assembly for shaanxi automobile delong vehicles is a sophisticated system comprising several integrated elements.
The Clutch Disc is the component that is sandwiched between the flywheel and the pressure plate. It is splined to the transmission’s input shaft, meaning it can slide along the shaft but must rotate with it. The disc is lined with high-friction material on both sides, often referred to as clutch facings. These facings are responsible for generating the grip necessary to transmit torque. A crucial feature of the disc is its torsional dampers, which are small springs that absorb and dampen torsional vibrations from the engine, ensuring smoother engagement and protecting the drivetrain from shock loads.
The Pressure Plate is a heavy, spring-loaded cast iron or steel component that applies a uniform clamping force to the clutch disc against the flywheel. It is this clamping force that creates the friction coupling, allowing power to flow. In the context of a pull-type clutch, the pressure plate assembly is designed with a set of levers or fingers that are actuated by being pulled, rather than pushed. The 430mm measurement refers to the outer diameter of the pressure plate and the clutch disc, indicating a large surface area capable of handling high torque levels.
The Diaphragm Spring is the heart of the clamping mechanism. It is a single, round, Belleville-style spring that, when in its resting state, applies the massive clamping force required. When the clutch is disengaged, this spring is deflected, releasing the clamping pressure. The design of the diaphragm spring in a pull-type clutch assembly is configured to be actuated from the opposite side compared to a push-type, making it integral to the pull-action.
The Release Bearing, also known as the throw-out bearing, is the component that translates the driver’s input from the clutch pedal into mechanical action on the clutch assembly. For a pull-type clutch, this is a pull-type release bearing. It is a unit that includes the bearing itself and a sleeve or collar. When the clutch is actuated, it pulls on this bearing assembly, which in turn pulls the diaphragm spring’s fingers to disengage the clutch.
The Flywheel, while technically part of the engine, is an essential interface for the clutch. It is a large, heavy mass attached to the engine’s crankshaft that provides a smooth, machined friction surface for the clutch disc to engage with. Its weight also helps to smooth out the power pulses from the engine.
The table below summarizes the primary function of each core component:
| Component | Primary Function |
|---|---|
| Clutch Disc | Transmits torque via friction, dampens vibrations. |
| Pressure Plate Assembly | Applies and releases clamping force on the clutch disc. |
| Diaphragm Spring | Provides the clamping force; actuated to release pressure. |
| Pull-Type Release Bearing | Converts hydraulic or cable force into a pulling action to disengage the clutch. |
| Flywheel | Provides a friction surface and engine smoothing. |
The Step-by-Step Operational Cycle
The operation of the 430mm pull clutch assembly for shaanxi automobile delong vehicles is a precise sequence of events that occurs every time the clutch pedal is depressed and released. Understanding this cycle is key to appreciating the elegance and efficiency of the pull-type design.
The Engaged State: Power Transmission
When the clutch pedal is fully released, the 430mm pull clutch assembly for shaanxi automobile delong vehicles is in its default engaged state. In this position, the diaphragm spring within the pressure plate assembly exerts its full force, clamping the clutch disc tightly between the pressure plate and the engine’s flywheel. This creates a solid friction lock. The engine’s crankshaft rotates the flywheel, which rotates the clamped pressure plate and clutch disc as a single unit. Since the clutch disc is splined to the transmission’s input shaft, this rotational force is transmitted directly into the transmission, ultimately driving the wheels. This state is for normal driving, where power is flowing from the engine to the drivetrain without interruption.
The Disengagement Process: Interrupting Power Flow
The process of disengagement begins when the driver presses the clutch pedal. This action is typically transmitted hydraulically, though some systems may use a cable mechanism. The hydraulic slave cylinder or mechanical linkage is positioned to act on the pull-type release bearing.
Unlike a push-type system where force is applied to push the bearing forward, in this system, the release mechanism pulls the bearing assembly rearward (away from the transmission). As the pull-type release bearing is pulled, it comes into contact with the internal tips of the diaphragm spring’s fingers. Pulling on these fingers causes the diaphragm spring to deflect. This deflection acts like a toggle, where the outer rim of the spring pulls the pressure plate away from the clutch disc. This action releases the clamping force. With the pressure plate retracted, the clutch disc is no longer clamped against the flywheel. It ceases to be driven by the engine, thus interrupting the power flow to the transmission. This allows the gearbox to be shifted in or out of gear without grinding, as the input shaft is no longer under load from the engine. This entire process is what makes clutch disengagement in a pull-type system distinct and highly effective for high-load applications.
The Re-engagement Process: Smoothly Restoring Power
Re-engagement is the controlled process of reconnecting the engine to the transmission. It begins when the driver starts to release the clutch pedal. Hydraulic pressure decreases, or cable tension is reduced, allowing the pull-type release bearing to move back towards its resting position. This gradual release reduces the pulling force on the diaphragm spring’s fingers. The diaphragm spring, due to its inherent elasticity, begins to return to its original, non-deflected shape. As it does so, its outer rim once again applies increasing pressure on the pressure plate, which in turn clamps the clutch disc against the flywheel.
The initial phase of this clamping is where smooth engagement is critical. The friction surfaces of the clutch disc begin to slip against the flywheel and pressure plate, gradually bringing the disc (and the transmission input shaft) up to the engine’s speed. The driver modulates this process by carefully controlling the pedal release. The large 430mm diameter of the assembly provides a substantial surface area for this friction, allowing for the smooth absorption and transfer of torque without excessive judder or grab. Once the pedal is fully released and the speeds are synchronized, slippage ceases, and the assembly is fully engaged, restoring a solid mechanical connection for power transmission. The quality of the components and the precise design of the clutch cover assembly are paramount in ensuring this process is consistent and reliable over the long term.
Key Advantages of the Pull-Type Design in Heavy-Duty Applications
The choice of a pull-type design for the 430mm pull clutch assembly for shaanxi automobile delong vehicles is not arbitrary; it is a deliberate engineering decision that offers several distinct benefits, particularly in the context of heavy-duty trucking.
Enhanced Clamp Load and Torque Capacity. The mechanical leverage advantage in a pull-type configuration allows for a higher clamp force to be generated for a given pedal effort, or conversely, allows for a manageable pedal effort even with a very high clamp load. This high clamp load is directly related to the assembly’s ability to transmit high levels of torque without slipping. This makes the 430mm pull clutch assembly for shaanxi automobile delong vehicles an ideal heavy-duty truck clutch component, capable of handling the substantial torque output of large diesel engines, especially when under load.
Reduced Pedal Effort. The leverage advantage inherent in the pull-type design translates to a noticeably lighter clutch pedal feel for the driver. In stop-and-go traffic or during long hauls that require frequent gear changes, this reduction in physical effort can significantly decrease driver fatigue, contributing to both comfort and safety. This characteristic is a key selling point for those sourcing clutch parts for delong trucks with driver ergonomics in mind.
Improved Durability and Heat Dissipation. The pull-type clutch system often incorporates a design where the release bearing retracts completely away from the diaphragm spring fingers when the clutch is engaged. This eliminates constant contact and minimizes wear on both the bearing and the spring, leading to a longer service life. Furthermore, the robust construction required for the pull-action, combined with the large 430mm diameter, provides a greater mass and surface area for dissipating the immense heat generated during clutch engagement, a critical factor in preventing clutch failure and ensuring reliable performance.
Compact Design. The actuation mechanism of a pull-type clutch can be more compact, which is beneficial in vehicles where space between the engine and transmission is at a premium. This allows engineers to design a powertrain that is both powerful and space-efficient.
The following table contrasts the general characteristics of pull-type and push-type clutches in a heavy-duty context:
| Feature | Pull-Type Clutch | Push-Type Clutch |
|---|---|---|
| Actuation Force | Pulls the release bearing away from the transmission. | Pushes the release bearing towards the transmission. |
| Pedal Effort | Generally lower for a given clamp load. | Generally higher for a comparable clamp load. |
| Torque Capacity | High; well-suited for high-torque applications. | Good, but may be limited by release mechanism stress at very high loads. |
| Release Bearing Wear | Reduced, as bearing retracts from contact in engaged state. | Can be higher, as design may allow for constant contact. |
| Common Applications | Heavy-duty trucks, high-performance vehicles. | Lighter-duty trucks, passenger vehicles. |
Maintenance and Sourcing Considerations
For wholesalers and buyers, understanding the operational principles of the 430mm pull clutch assembly for shaanxi automobile delong vehicles directly informs procurement and inventory strategies. Recognizing the signs of wear and knowing what to look for in a replacement part is crucial.
Common indicators that a clutch replacement may be necessary include slipping (engine RPM increases without a corresponding increase in vehicle speed), difficulty shifting gears, a clutch pedal that feels spongy or sticks to the floor, and unusual noises during disengagement. When sourcing a replacement, it is imperative to ensure compatibility with the specific model and engine of the vehicle. The term 430mm pull clutch assembly for shaanxi automobile delong vehicles should be considered a key identifier, but verifying against the vehicle’s VIN or engine serial number is always recommended practice.
Quality is paramount. A premium clutch kit should include not only the clutch disc, pressure plate, and release bearing but also often an alignment tool and may include a pilot bearing. The materials used for the clutch facings should be designed for high heat tolerance and consistent friction characteristics. The diaphragm spring should be made from high-grade steel to resist fatigue and maintain its clamping force over thousands of cycles. For buyers, emphasizing the importance of sourcing from reputable manufacturers who adhere to strict quality control standards cannot be overstated. A reliable clutch assembly minimizes vehicle downtime, reduces the frequency of clutch repairs, and ensures the vehicle can consistently perform its intended heavy-duty hauling tasks.
In conclusion, the 430mm pull clutch assembly for shaanxi automobile delong vehicles is a masterclass in mechanical engineering, tailored for resilience and performance. Its pull-type operation provides a robust, high-torque-capacity solution that offers reduced driver effort and enhanced durability. From the initial engagement that sets the vehicle in motion to the seamless transitions between gears, every component within the assembly plays a critical role. For those in the business of supplying parts for these formidable trucks, a deep technical understanding of this system is not just beneficial—it is fundamental to providing value, ensuring customer satisfaction, and supporting the relentless demands of the transportation industry.
 English
English русский
русский




 English
English  No.25, Hu Chuang Road, New District Industrial Park, Suzhou, Jiangsu, China.
No.25, Hu Chuang Road, New District Industrial Park, Suzhou, Jiangsu, China.  +86-13338663262
+86-13338663262 
