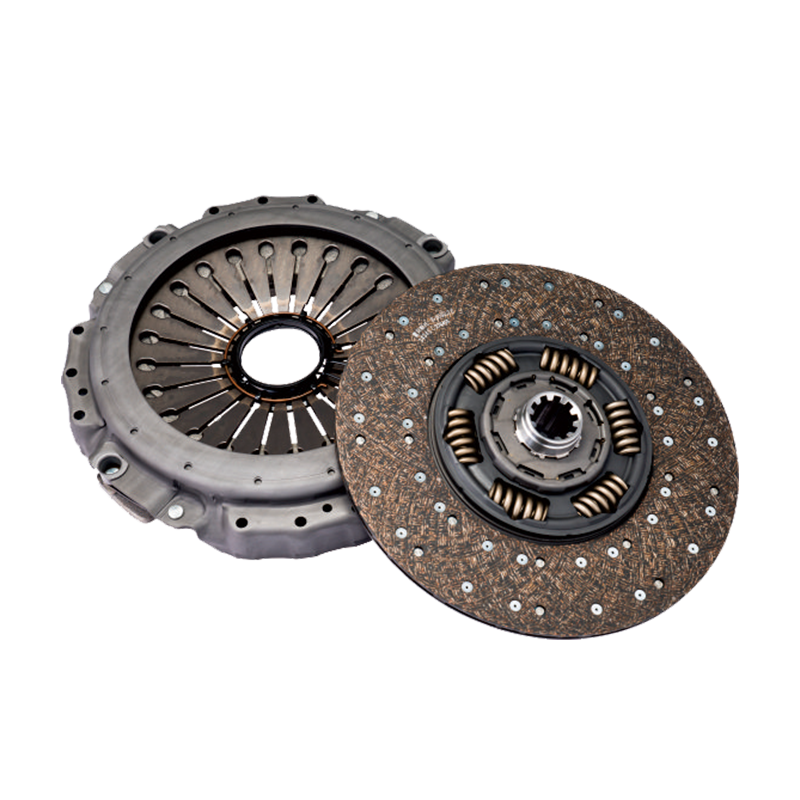
The 430mm pull type clutch cover assembly kit for FAW Jiefang vehicles plays a critical role in transmitting torque from the engine to the transmission system in heavy-duty trucks. Its reliability directly influences vehicle performance, fuel efficiency, and operational safety. Among the most common operational issues encountered with this clutch assembly is slipping, a condition in which the clutch fails to fully engage, causing a loss of power transmission.
The role of 430mm pull type clutch cover assembly kit for FAW Jiefang vehicles
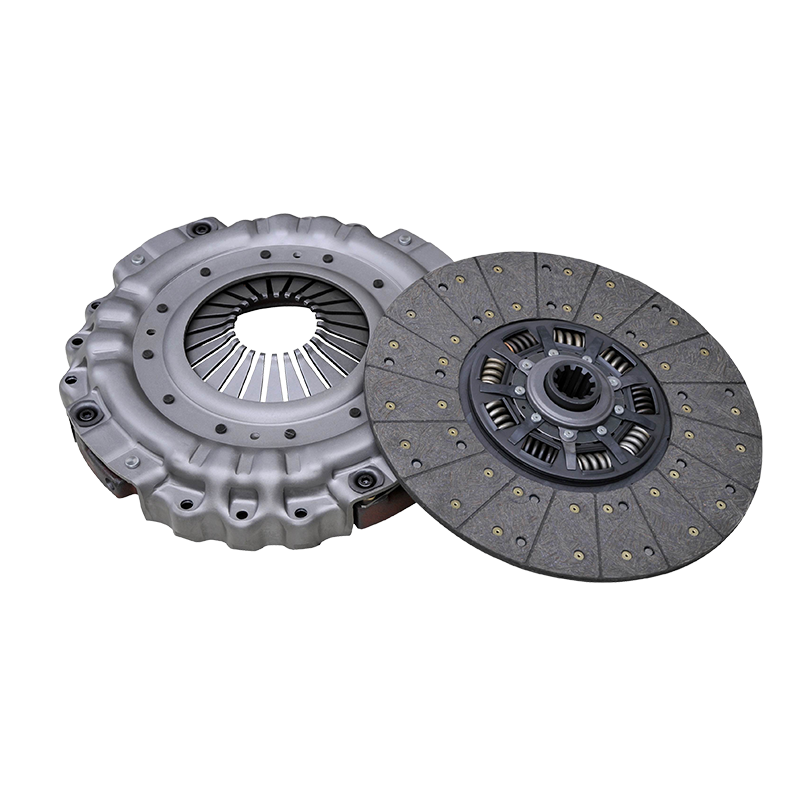
The 430mm pull type clutch cover assembly kit for FAW Jiefang vehicles consists of several critical components: the pressure plate, diaphragm spring, release bearing, and cover housing. Each part contributes to the smooth engagement and disengagement of the clutch system. The pressure plate applies force to the friction disc, enabling power transfer, while the diaphragm spring ensures consistent clamping pressure. Any deviation in these components can result in clutch slipping, which manifests as a delay in vehicle acceleration, increased engine revs, or unusual noises.
The functional integrity of the clutch assembly is influenced not only by component quality but also by external factors such as driving conditions, maintenance practices, and operating environment.
Mechanical factors leading to slipping
Worn friction disc
One of the primary mechanical causes of slipping in the 430mm pull type clutch cover assembly kit for FAW Jiefang vehicles is a worn friction disc. Over time, friction materials degrade due to continuous engagement cycles, heat, and load stress. Signs of a worn disc include reduced clamping force, visible surface glazing, and uneven wear patterns. A worn friction disc directly reduces the torque transfer capability, causing noticeable slippage.
Weak diaphragm spring
The diaphragm spring is responsible for applying uniform pressure to the friction disc. A weakened or fatigued spring loses its tension over time, resulting in insufficient clamping force. This mechanical failure can be caused by prolonged heavy-duty usage or exposure to excessive temperatures. Once the spring fails to maintain optimal pressure, slipping occurs, particularly under high load conditions.
Improper installation
Incorrect installation of the 430mm pull type clutch cover assembly kit for FAW Jiefang vehicles is another significant factor. Misalignment of the cover assembly, torque misadjustment, or uneven tightening of bolts can compromise the uniform distribution of pressure. This scenario not only increases wear on friction surfaces but also reduces engagement efficiency, ultimately causing slippage.
Contamination of friction surfaces
Friction surfaces contaminated with oil, grease, or dirt can dramatically reduce the coefficient of friction between the pressure plate and the clutch disc. Such contamination is often observed in engine oil leaks, transmission fluid leakage, or maintenance errors. Contaminated surfaces prevent full torque transfer, leading to noticeable slipping during vehicle operation.
Table 1: Mechanical factors and their effects on slipping
| Mechanical factor | Effect on clutch performance | Observed symptoms |
|---|---|---|
| Worn friction disc | Reduced torque transfer | Slipping, delayed acceleration |
| Weak diaphragm spring | Insufficient clamping pressure | Increased engine revs, vibration |
| Improper installation | Uneven pressure distribution | Uneven wear, noise |
| Contaminated friction surfaces | Reduced coefficient of friction | Slippage under load |
Environmental and operational influences
High temperature operation
Heavy-duty trucks equipped with 430mm pull type clutch cover assembly kit for FAW Jiefang vehicles frequently operate under high-temperature conditions. Excessive heat can soften friction materials and reduce spring tension, accelerating wear and reducing torque capacity. Continuous operation under such conditions can significantly shorten clutch life and increase the likelihood of slipping.
Overloading and heavy-duty driving
Frequent overloading and high-torque driving can lead to excessive stress on the clutch system. The 430mm pull type clutch cover assembly kit for FAW Jiefang vehicles is designed for specific load parameters, and repeated overload conditions cause accelerated wear of friction surfaces, deformation of the diaphragm spring, and premature clutch failure.
Environmental contamination
Dust, sand, and road debris can infiltrate the clutch housing, especially in regions with harsh terrain or extreme weather. Such contamination introduces abrasive particles between the friction disc and pressure plate, increasing wear and reducing the clutch’s engagement efficiency.
Operator behavior
Improper driving habits, such as riding the clutch or excessive slipping during gear changes, can significantly accelerate wear. Prolonged partial engagement leads to increased friction heat, glazing of the disc, and a gradual reduction in clamping force, all contributing to slipping.
Table 2: Environmental and operational factors contributing to slipping
| Factor | Impact on clutch function | Recommended prevention |
|---|---|---|
| High temperature operation | Softening of friction material, spring fatigue | Monitor temperature, allow cooling periods |
| Overloading | Excessive wear, deformation | Adhere to vehicle load limits |
| Dust and debris | Abrasive wear, surface damage | Use protective covers, maintain housing integrity |
| Improper driving | Premature wear of disc and spring | Operator training, avoid riding clutch |
Signs and symptoms of clutch slipping
Recognizing slipping early is crucial for preventing further damage. The most common indicators include:
- Delayed acceleration despite high engine revs
- Unusual engine noise or vibration during gear engagement
- Burnt smell from friction surfaces
- Reduced fuel efficiency due to incomplete power transfer
In addition, vehicle monitoring systems may detect inconsistent torque output or abnormal engine load patterns, which are indicative of clutch engagement issues.
Diagnosis and inspection methods
Visual inspection
A careful visual examination of the 430mm pull type clutch cover assembly kit for FAW Jiefang vehicles can reveal glazing, uneven wear, or contamination. Removing the assembly allows assessment of the friction disc, diaphragm spring tension, and cover alignment.
Functional testing
Functional testing involves checking torque transfer under controlled conditions. A slipping clutch will show loss of power transmission and higher than expected engine revs without corresponding vehicle acceleration.
Maintenance records analysis
Reviewing maintenance logs provides insight into operational stress, replacement history, and prior issues. Patterns of slipping often correlate with prolonged high-load operation, delayed maintenance, or repeated contamination events.
Preventive measures
Regular maintenance
Routine inspection and replacement of worn components are essential to maintain clutch performance. Scheduled checks of friction discs, diaphragm springs, and housing alignment can prevent slipping.
Proper installation procedures
Adhering to manufacturer-recommended installation steps, including correct torque settings and alignment, ensures uniform pressure distribution and minimizes premature wear.
Driving behavior management
Training operators to avoid riding the clutch and manage gear engagement under heavy loads reduces heat buildup and extends clutch life.
Environmental protection
Ensuring proper sealing and protecting the clutch housing from dust, debris, and fluid contamination can prevent abrasive wear and reduce the risk of slipping.
Conclusion
Slipping in 430mm pull type clutch cover assembly kit for FAW Jiefang vehicles arises from a combination of mechanical, environmental, and operational factors. Worn friction discs, weak diaphragm springs, improper installation, contamination, excessive heat, overloading, and operator behavior all contribute to reduced engagement efficiency. Through proactive maintenance, proper installation, and careful operation, vehicle operators can significantly reduce the risk of clutch slipping and ensure long-term performance.
FAQ
Q1: How can I tell if the 430mm pull type clutch cover assembly kit for FAW Jiefang vehicles is slipping?
A1: Signs include delayed acceleration, high engine revs without speed increase, unusual noises, and a burnt smell from friction surfaces.
Q2: How often should I inspect the 430mm pull type clutch cover assembly kit for FAW Jiefang vehicles?
A2: Regular inspections should occur based on vehicle mileage and load conditions, typically every 20,000–30,000 km for heavy-duty use.
Q3: Can a slipping 430mm pull type clutch cover assembly kit for FAW Jiefang vehicles be repaired?
A3: Minor surface contamination can sometimes be cleaned, but worn friction discs and weak springs usually require replacement.
Q4: Does heavy-load driving accelerate slipping in 430mm pull type clutch cover assembly kit for FAW Jiefang vehicles?
A4: Yes, exceeding load limits increases friction surface wear and stress on the diaphragm spring, leading to earlier slippage.
Q5: How can operator behavior reduce the risk of slipping?
A5: Avoid riding the clutch, minimize partial engagement, and follow proper gear-shifting procedures to reduce heat and wear.
References
- FAW Jiefang Technical Manual: Clutch System Maintenance Guidelines.
- Heavy Vehicle Maintenance Best Practices, International Transport Engineering Journal, 2021.
- Smith, J., “Clutch Slippage in Heavy-Duty Trucks: Causes and Prevention,” Automotive Engineering Review, 2020.
 English
English русский
русский




 English
English  No.25, Hu Chuang Road, New District Industrial Park, Suzhou, Jiangsu, China.
No.25, Hu Chuang Road, New District Industrial Park, Suzhou, Jiangsu, China.  +86-13338663262
+86-13338663262 
